Design4Innovation is aiming to influence business and innovation support programmes for SMEs in the European Union to include design as a tool for user-centred and market-driven innovation. In this series of articles, we are going to explore different types of support instruments to better understand where design can fit best.
Business Support Ecosystem
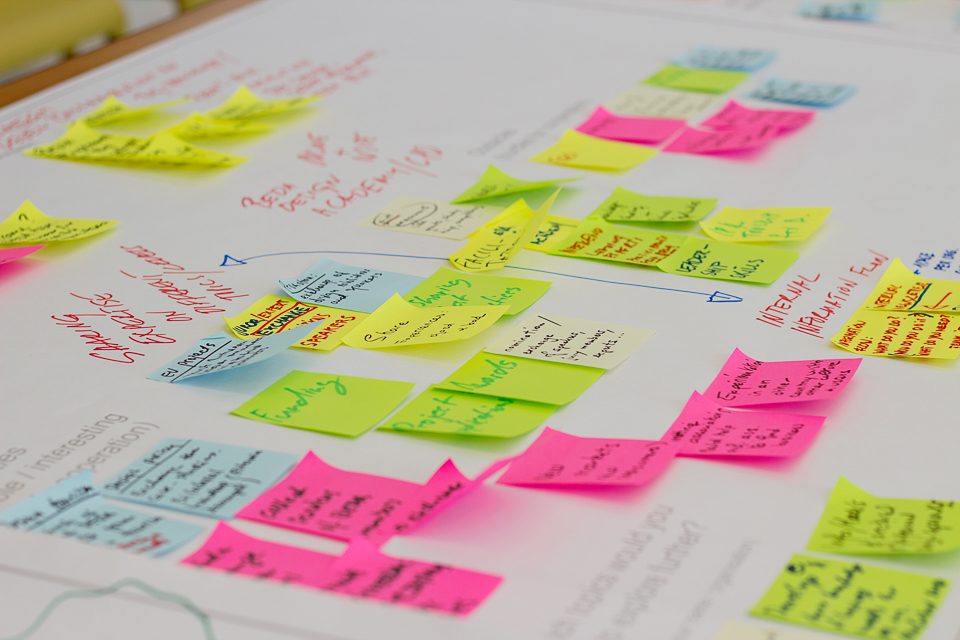
Fig 1. Business Support Ecosystem (TRINNO Project)
Business support programmes are interventions aimed to address systemic inefficiencies and market failures, in order to stimulate entrepreneurship, job creation, innovativeness and economic growth. Learning from other Interreg Europe project, we found the concept the Business Support Ecosystem extremely useful. Developed by TRINNO project (Business Ecosystem for Tradition and Innovation), the model presents different forms of business support in three categories of instruments: soft support, funding and physical infrastructure. The instruments are also grouped according to the phases of enterprise maturity, namely: stand-up, start-up, scale-up and mature. The model identifies also an ‘exit’ phase, when a business owner decides to cash out a previously made investment.
In this article, we will discuss different ‘hard’ support mechanisms (financial services) related to the five life-cycle phases of a company. However, it is important to emphasize that while some instruments are specific to the business maturity, the others can be applied on multiple stages of company’s life cycle.
Stand Up
A stand up phase refers to the time when an individual or a group of people start looking for entrepreneurial models and skills in order to create a new company. Vocational training as well as business planning support are the most common instruments applied on that stage. Young entrepreneurs and graduates can often use carrier advice and pre-incubation services offered by universities and research centres.
There is no direct financial support, apart from vouchers for professional advisory or mentoring services. Aspiring entrepreneurs usually fund this initial stage from their own savings or the ‘bank of family and friends’.
Start-up
Contrarily to the stand-up phase, this one requires a mobilisation of significant resources in terms of both capital and labour. Launching ventures have a whole range of support mechanisms to choose from, including infrastructural support (such as incubators, technological parks, and subsidized co-working spaces) and soft support tools (specialist advisory services, matchmaking, mentoring) that we will describe in more detail in the next article.
With respect to financial instruments, grants and low-interest loans backed by public funds, such as start-up loans, are the most common support mechanisms. Starting businesses can also apply for venture investment or mezzanine financing (hybrid of debt and equity financing) from publicly managed funds offered by investment banks or similar bodies. Other forms of financial support for start-ups include micro-credit and bank loan guarantee. Business funding programmes are often perceived as too complex to comprehend, and too bureaucratic and time-consuming for a fast-paced reality of business and tech innovation. There is a big opportunity for service design, to re-create business support offer with innovators needs guiding the process.
At this point, it is also worth mentioning the alternative sources of funding, such as for instance crowdfunding or peer-to-peer lending that in recent years have gained considerable popularity among innovative undertakings. Through a funding campaign, starting entrepreneur can test the business concept, build the customer group and could raise the investment at much lower premium than in the bank.
Article continued in the next news piece...
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
 Pedro Asti, MA student in European Studies at the University of Padua.
Pedro Asti, MA student in European Studies at the University of Padua.
Among other subjects, I am particularly interested in innovation within the public and private sectors.
I am a strong believer that creativity, critical thinking and imagination are crucial skills for modern society to prosper and advance, as well as keys to solve today's complex problems all over the word.