
InnoHEIs impact on regional innovation policies
The collaboration in the InnoHEIs project has positively impacted innovation and research policies of participating regions.
InnoHEIs aims at enlarging the role of higher education institutions (HEIs) and their research and innovation infrastructure. How can they act as key stakeholders for regional innovation development?
Watch the video to meet the partners and learn more about the project:
Fostering entrepreneurship and creativity in regions
Fostering entrepreneurship and creativity brings many benefits to higher education institutions and regions. InnoHEIs addresses the challenge to enhance the role of higher education institutions and their research and innovation infrastructure.
Enabler of the entrepreneurship discovery process
This role can be filled in as an enabler of the entrepreneurship discovery process (EDP). The entrepreneurship discovery process is an inclusive and interactive bottom-up process. Participants from different environments, such as policy, business and academia are discovering a potential of new activities and opportunities that emerge through this interaction.
Integration of entrepreneurial knowledge
Higher education institutions and their research and innovation infrastructure can build partnerships thanks to their unique infrastructure and human capacities. Entrepreneurial knowledge is often fragmented and distributed over many organisations, companies, universities, clients and users. Higher education institution can support the integration of the entrepreneurial knowledge.
Remove barriers and enhance collaboration
Thus, InnoHEIs partners look at possibilities to mobilise higher education institutions and their research and innovation infrastructure for regional innovation development. Their aim is to remove barriers among different types of higher education institutions and their research and innovation infrastructure. And enhance their cross-institutional and cross-sectoral collaboration.
€1,960,697.00
Research and innovation
InnoHEIs aims to improve the usage and employment of innovation infrastructure. This is achieved through better involvement of its users and customers. Next to that the collaboration between science, industry and public will be enhanced.
Partners will collaborate seeking to improve the performance of higher education institutions and their research and innovation infrastructure. They will respond to the regional needs and demand. To solve regional societal challenges they will use:
Expected outputs of the project:
Fifty policy learning events will be organized:
Thorough regional diagnosis in partner regions will be conducted identifying existing good practices. Partners estimate that at least 16 good practices will be analysed and at least 210 people will increase their professional capacities.
Cover image: Gerd Altmann via Pixabay
The Policy instrument addressed is OP Priority axe 1: Innovation and within this priority the specific objective “Fostering knowledge development” and the following activity of this objective: “Knowledge development and research by businesses working in partnership with knowledge institutions or other businesses”.
These knowledge institutions are in many cases ‘owners’ of large Research and Innovation Infrastructure facilities in the Northern Netherlands. As mentioned in the RIS3 of the Northern Netherlands, an important regional asset (and because of that an import part of the Smart specialisation) is the possibility of the employment (and in many cases already the availability) of large scale Living Labs. These facilities and their employment in RIS3 are of key importance for the development of the Northern Netherlands. The policy instrument aims to strengthen the employment of RII. Until now, RII is not fully used by or is accessible for regional SME’s and other organisations. And although several calls based on the policy instrument try to improve the use of RII, the instrument is not ‘intelligent’ enough to effectively use the potential of RII in the region. The use of (regional) RII on an EU level in an effective and efficient way is barely developed accordingly the necessary enabling policies are barely developed. Via the international partnership of InnoHEIs SNN will work on improvement of the policy as well on regional as on EU level.
One of the programmes that is financed by the The ERDF 2014-2020 for Catalonia priority axis 1 "Research and innovation" is CATLabs is the brand new strategy plus instrument of the Catalan Government to put together the agents of the quadruple helix to find challenges, design projects, implement them, monitor and evaluate them, and escalate them to reach the market. Also, the improvement of performance of high education institutions and their research and innovation infrastructure is included in the strategy. To implement the strategy, from 2015 to 2020 (and after under the new programming period that is being designed) the instrument gives some financial incentives (mostly subsidies) for pilot projects to be developed under this scope, selecting challenges that are tackled by the Catalan Smart Specialisation Strategy (RIS3CAT). This instrument is co-funded by the ERDF 2014-2020 for Catalonia, under its priority axis one (research and innovation) and it aims at being the start of the promotion of open innovation under the quadruple helix model in Catalonia.
Operational Programme ERDF-ESF Centre 2014-2020, Axis 1: a knowledge-based society (OT 1 is directly linked with the RIS3 objective to increase the critical mass, visibility and attractiveness of competence centres in the 5 priorities areas and implementting this policy. Furthermore, a study has been conducted by the Join Research Center (JRC) of the European Commission the strengthening the role of Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) in regional partnerships. CVL Region is one of the 5 pilot region that have benefited from this initiative called HESS. The policy perceives HEIs and its’ infrastructure as central to smart specialisation, in particular for the development and retention of human capital, application of innovation, development of new innovative products and services as well as an environment for promotion of entrepreneurship. The mid-term result has fostered the awareness of the policy makers as well as the HEIs themselves to the necessity to encourage HEIs to better contribute to S3 implementation.
The Managing authority of Finnish ERDF programme is the Ministry of Economic Affairs and Employment. It channels the funding to regional authorities. At a regional level, a Regional Management Committee (RMC) is coordinating the implementation of national and EU co-financed programmes. Regional development targets are defined in the Regional Strategic Programme covering a four-year period. It includes the development objectives for regional possibilities, needs, culture and other unique features of the region, a description of projects that are essential to the development of the region and other key measures as well as plans for funding the programme. One of the main goals of this funding is strengthening research, technological development and innovation (Priority axis 2). The goals of InnoHEIs supports development of the national specific objectives 4.1 Developing research, competence and innovation clusters that draw from regional strengths and 5.1 Strengthening innovation work in companies. Regions has been in forefront in developing open innovation platforms for the demonstration of new innovations of public and private organisations and for start-ups, but it has not been able to support as efficiently technology transfer for mature businesses.
The Mid Sweden Region is focussing on developing research and innovation ecosystems connecting industry, academia and the public sector around important areas, like “Forest as a resource”, “Industrial information technology and digital services”, “Tourism” and “Sports and Health”. Environmental, economic and social sustainability are important horizontal criteria in all areas. There are also important well recognised research in social science and humanities, genus, democracy and political science, sensor based services, digital printing and digital information services. Currently there is a strong focus on scaling up the environmental research and the development of new methods to reduce CO2 emissions. Connected to the Goal 1B investment priorities and the goal 1B innovation priorities, it is considered important to increase the investments in research and development which is low compared to other regions and to increase the commercialisation of research. The ERDF policy instrument for innovation and growth needs to be improved by adding the dimension of social science and humanities into technology driven innovation programs utilising the cross scientific approaches given by mixing technology driven development and research with social science and humanities, digital information services in a structural way.
Priority 1. Strengthening research and development and innovation Investment priority 1.1 Enhancing research and innovation (R&I) infrastructure and capacities to develop R&I excellence, and promoting centres of competence, in particular those of European interest. Specific objective 1.1.1 Promoting more active use of the existing and new research, development and innovation infrastructure. This investment priority intends to support creation, updating and development of the RDI infrastructure of units (centres of excellence, technological centres), in particular infrastructure focused on the commercialisation of experimental development activities and their results, promoting public-private cooperation in the field of RDI as well as upgrading and development of RDI infrastructure for the implementation of the Smart Specialisation Strategy, including the development and implementation of non-technological solutions focused on more efficient RDI activities.
Regional Operational Programme of the Silesian Voivodeship (ROP WSL) 2014-2018 is the regional investment programme for economic and entrepreneurship development, growth, employment, education and training. This multi-fund ERDF/ESF OP aims to fulfill the Silesia 2020 Development Strategy. It runs alongside the regional RIS3 (planned updates in 2019-20). The OP provides funding for ten thematic objectives. Axis I supports the Modern Economy (ERDF). It funds activities aimed at increasing market value of R&D, increased enterprise R&D, improving the pro-innovation environment of enterprises. The beneficiaries are: enterprises, research units and business environment institutions. Priority axis 1.1. is dedicated to key regional research infrastructure (construction and equipment of research infrastructure for research in the smart specialization areas). Research infrastructure supported under the projects does not replicate existing resources and completes existing R&D infrastructure and should be adequate to planned research and development agenda. Access to infrastructure is provided to a range of users on a transparent and non-discriminatory basis. The Regional Innovation Strategy of the Śląskie Voivodeship is a policy of supporting the innovative development of enterprises and the science sector in the area of defined areas of smart regional specializations

The collaboration in the InnoHEIs project has positively impacted innovation and research policies of participating regions.

Projects can also provide a way to influence regional policies

The Final InnoHEIs Conference was organized by Silesian University and took place on April 26 in Katowice, Poland

As part of the European Funds for Silesia 2021-2027, it is planned to support scientific units for projects in the field of research infrastructure.

InnoHEIs project achievements will be presented in the UIIN Conference 2023 with the topic SIXLabs Playbook supporting Knowledge Valorisation Process of SMEs

From the 9th till the 11th of May, InnoHEIs partners visited the Lithuanian partners Ministry of Education, Science and sport, and Lithuanian Innovation Centre....
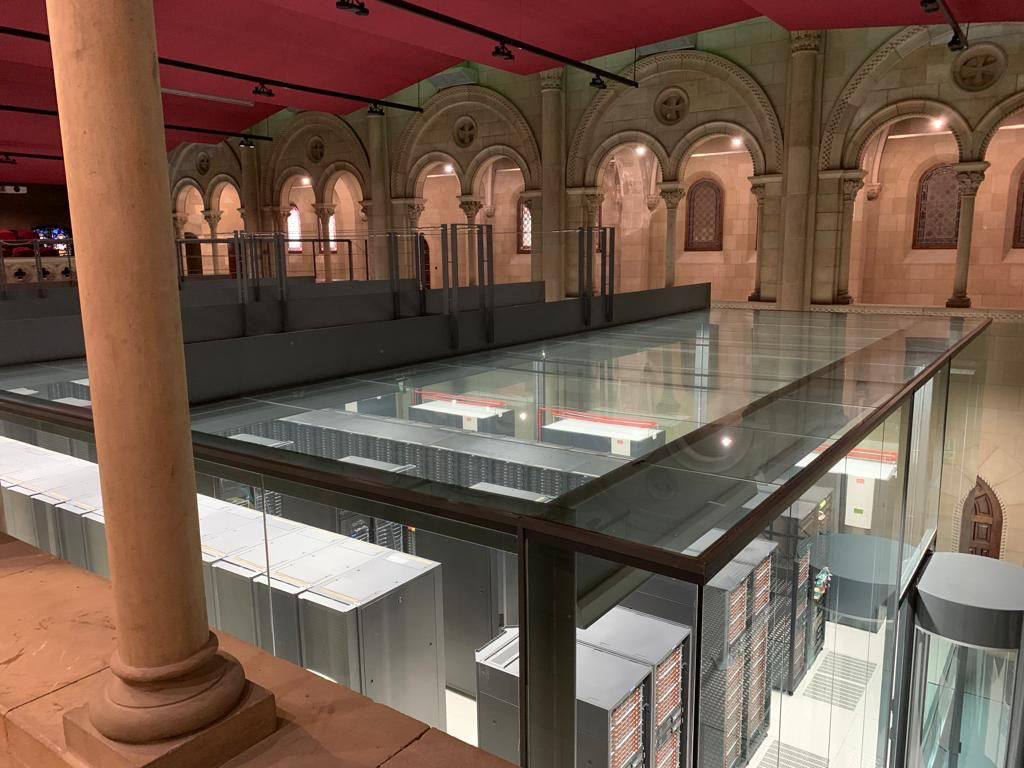

On 29 March, partners kicked off with the meeting by getting to know the Catalan framework for RDTI polices, and they got to know the activities of two major
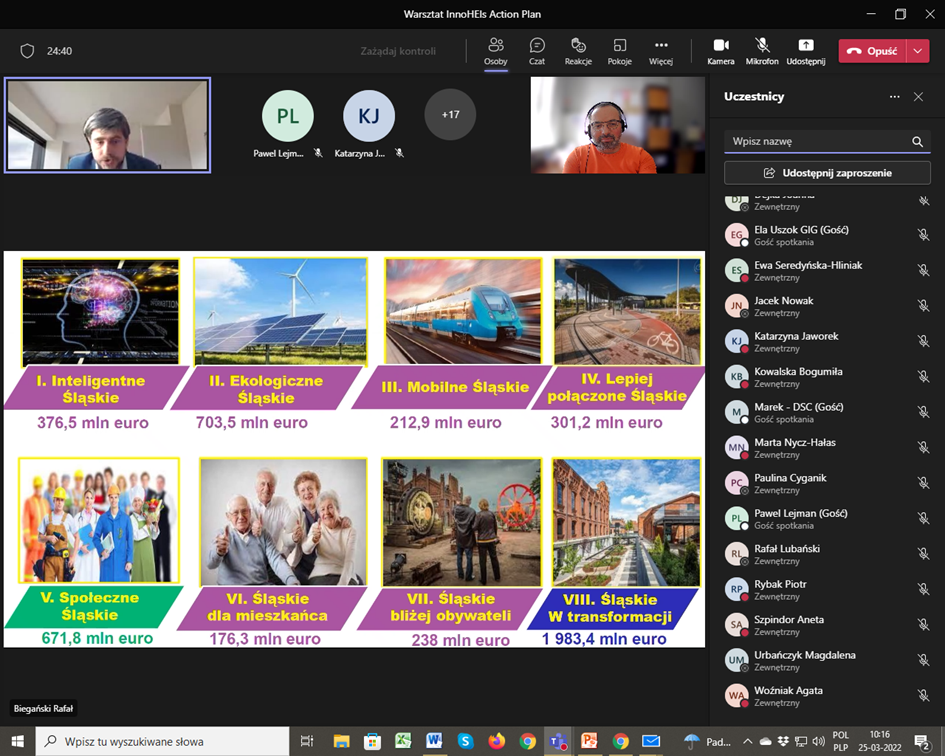
On March 25, 2022, the Marshal's Office of the Silesian Voivodeship together with the Central Mining Institute organized a workshop meeting addressed to enterpr...

The project is committed to regular dialogue with its’ contributors. Various topics were discussed during the Finnish stakeholder meeting in January.
On Wednesday 26 January 2022, the Autonomous University of Barcelona hosted the 5th stakeholder meeting of the InnoHEIs project in Catalonia.