
ERUDITE | Our partners said
Short video statements about the regional impact of ERUDITE project.
ERUDITE in 1 video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UwjAneu9D9c
COVID-19 has accelerated the use, visibility and diffusion of digital tools and services; confinement measures have encouraged a long-term move to remote working, learning and e-services. This is of particular importance in rural and peripheral regions.
The ERUDITE consortium continues its 5-year work and undertakes an exchange programme to evaluate the impact of the crisis on the development and operation of digital services and develop measures to respond.
€2,528,785.00
Research and innovation
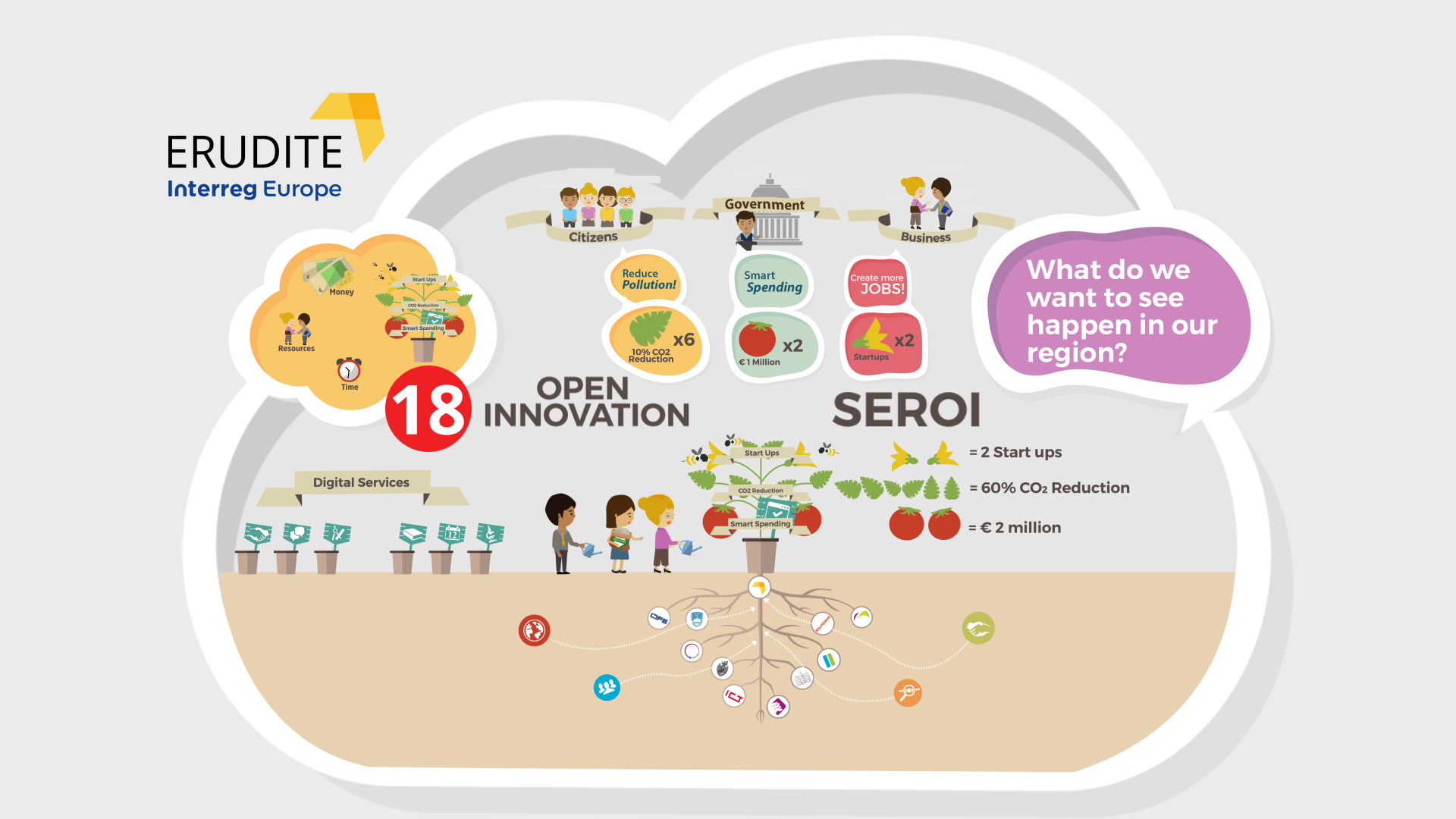
ERUDITE changed the way our partners approach service design and implementation by creating simple value-led roadmap, that we call SEROI+, with four steps that constitute the building blocks for service co-creation for smart rural communities and ecosystems:
1. Define policy or practice goals for the services;
2. Identify and engage relevant stakeholders and define their goals;
3. Co-design the service;
4. Set indicators and values, estimate and then monitor social, economic and environmental return on investment.
A dedicated section of the website to SEROI+ has been created https://www.interregeurope.eu/erudite/seroi-documents/
At European level through its contribution to the ENRD Thematic Working Group on Smart Villages ERUDITE made a significant congtribution to advancing the theory and pratice of SMART Rural Territories. See the dedicated section https://www.interregeurope.eu/erudite/smart-villages/ and the https://enrd.ec.europa.eu/enrd-thematic-work/smart-and-competitive-rural-areas/smart-villages_en . In the context of this Group ERUDITE co-organised the 8th-thematic-group-meeting in the village of Lormes in the Nièvre https://enrd.ec.europa.eu/news-events/events/8th-thematic-group-meeting-smart-villages_en
In the Library section you can find a selection of projects developed through the project in the 'ERUDITE Projects' folder
To help better communicate the results of the ERUDITE project a our partner the University of Ljubljana created a dedicated video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1X5AME0dz1s&t=115s
Each partner selected a service for monitoring in Phase Two where key indicators and values were selected by stakeholders to monitor and measure the social, economic and environmental impact the new service would have.
In the Innovation Priority Objective 1.1.4 of the Regional strategy of South Ostrobothnia it is stated that developing new innovative services, piloting them and implementing them is one of the aims of the region. ”E-service is a service that is provided via electronic interface and completely or partially performed electronically and where the end-user plays an active role in accessing and contributing to the performance and effectiveness of the service. According to the strategy, both private and public services are targeted. The aim is to enhance innovation and renew the services for better economic and social productivity. From the regional development viewpoint the target is necessary in order to improve growth prospects and improve the range and scope of services. However the priority and targets needs to be clarified and practical solutions need to be introduced from other European regions in order to ensure the best value for the region. Secondly whilst partnership working is at a good level, the Open Innovation process supported by Social and Economic Return on Investment Studies (SEROI), will enable the region to improve multi-stakeholder skills and awareness of innovation processes and potential.
The principal features are:
- to promote investment in product and service development, technology transfer, social innovation, public service applications, demand stimulation, networking, clusters and open innovation through smart specialisation;
- to develop links and synergies between enterprises, research and development centres and the higher education sector;
Objectives include: Networking and Strengthening of links and Synergies in the Innovation System; building a critical mass of different stakeholders, disciplines in priority areas of use identified in the RIS3. Motivation and engagement of experienced experts (from academia and industry), future entrepreneurs, students and general youth. As innovations and innovativeness are also an important factor to enhance the competitiveness of the public and third sectors, the country intends to support the innovations in these fields.
Slovenia needs to improve links between excellence, competences and potentials for development of new services and integrated solutions. Innovation activities must involve rural/peri-urban areas, currently lagging behind main urban centres. ERUDITE will support PO improvement through multidisciplinary exchange at European level by holding Open Innovation process supported by SROI; where the resulting multi-stakeholder design of digital services will improve targeting of investments towards projects that foster digital service development which maximise economic and social returns
In line with the 2014-2020 cohesion policy, NOP METRO is a new Operational Programme, financed by structural funds, approved on 14/7/2015 by the EC (Decision C(2015)4998)developed for the 14 Italian metropolitan cities established by law in 01/2015: Venice, Turin, Milan, Genoa, Bologna, Florence, Bari, Naples, Reggio Calabria, Rome, Cagliari, Catania, Messina and Palermo. In accordance with the European Urban Agenda, NOP METRO aims at turning metropolitan cities into more accessible, functional and sustainable places and make them more inclusive and inter-connected. The programme’s main objectives consist in spreading digital services, increasing sustainable mobility in urban areas, reducing energy consumption in public facilities and encouraging interventions for social inclusion. As Intermediate bodies, the metropolitan cities will be the directly in charge for the management of the funds. The City of Venice will therefore manage the budget of EUR 40,2 millions allocated to the Venice metropolitan area, composed of 44 small and medium municipalities. The ERUDITE project will support the City of Venice to boost the results of the NOP METRO priority “Metropolitan Digital Agenda” providing the methodology for: 1) activating open innovation processes to strengthen cooperation with local Innovation ecosystem players; 2) evaluating the impact of the investments to be financed by the NOP METRO in order to really meet social and territorial needs through digital service provision.
In the PI Access to High speed broadband and the development of new e-services to create growth and support structural changes has been identified as a highly prioritised area in the region. Increased access to, usage and quality in ICT is one of the thematic objectives with investment priorities that will improve ICT-applications for e-governance, e-learning, e-integration, e-culture and e-health.
The goal 2.c.1 for this is that new digital services are established and existing developed so that accessibility to private and public services improves The PO needs to be improved through the development of projects which optimize the use of available investment, social and economic impacts. With the increasing need to improve services, whilst stabilizing expenditure and raising e-literacy and innovation (social and economic) in a sparsely populated area digital solutions offer both an inclusive and efficient solution.
Currently however there is a low level of development and adoption of new e-services in the municipalities and the full potential of the existing ICT-infrastructure to create an efficient public organisation and services is not being used. Innovative processes are required to engage all stakeholders in developing solutions that meet their needs and which raise their digital skills/knowledge.
The project will address the Local Economic and Community Plan for County Donegal (LECP) which provides a 6 year framework to guide the strategic direction of future activity and relevant funding streams within Donegal. More concretely the measure concerned is the Donegal Digital Action Plan developed within the LECP process, which mandated that a separate Donegal Digital Action Team be setup to develop and implement the action plan.
The main goals of this instrument are:
1. Digitally-skilled communities co-creating services with the business and public sectors
2. An expanded digital cluster, home to indigenous and FDI companies.
3. A working, visible and relevant Donegal digital research and innovation environment.
The revision of previous relevant “digital” work carried out in County Donegal, a survey conducted among relevant stakeholders have served to identify the main areas to be improved:
• The low levels of research activity and adoption of emerging innovation approaches needed to be addressed in the medium term
• The need to facilitate the presence of highly visible innovation hubs in other towns that - in addition to working space - would provide facilities and resources for ICT training, remote campus, smart working, community capacity building, citizen living lab/open innovation initiatives.
Participation in ERUDITE will help to find new approaches that support the creation and enhancement of these objectives
The programme (source: ERDF, ESF, IKF; a total of 9,004.2 M EUR over 7 years) aims to stimulate the economies of the less developed regions in Hungary. The specific measure of the Program Measure 2.2. aims to develop links and synergies between enterprises, research and development centres and the higher education sector with focus on stimulating business investment and innovation, boosting economic growth, via strengthening links and synergies among businesses, research institutions, government and the local community. It explicitly promotes the establishment of strategic partnership networks, where ICT infrastructure could play a more enhanced role in involving the rural areas. The governance, performance and scope of these networks requires improvement
The instrument aims to trigger actions that will reinforce and expand regional innovation capacity based on the potential of involving, educating and empowering local business, citizens and public administration to become partners in the creation of digital services appropriate to their needs. In recent years heavy investment has taken place in ICT infrastructure in Hungary. The current challenges are how to convert it for the benefit of the rural areas, how to convert the hard infrastructure into social and economic advantages. Bringing more opportunities to disadvantaged regions, to achieve convergence, is a national priority.
The objective of the Policy Instrument (PI) is to ensure that the region’s citizens and businesses benefit fully from access to innovative, open, inter-connected and compatible e-services and which will be designed to be accessible using the range of evolving devices and which together will constitute a package of replicable and reusable services for the region.
The PI in particular envisages the development and deployment of open networked digital service platforms that are open and compatible. The aim is to mutualise and capitalize on the number of services on offer: primarily e-administration, e-education/training and apprenticeship share and facilitate their development and their use by the maximum number of private and public stakeholders.
The general public will also have access to a wider range of services better in tune with their daily needs.
The PI needs to be improved by developing projects that involve citizens and/or representative bodies, key public, private and third sector stakeholder organization in the development and delivery of new and improved e-services who will co-design them, taking into account and investment priorities and territorial needs established by Social Return of Investment. The region will learn how to really involve local stakeholders in the design of a of e-service platforms in order to foster innovation and maximize the social return of investment of the projects supported by the PI.

Short video statements about the regional impact of ERUDITE project.

Final meeting of the ERUDITE partnership in Lormes
good practices and lessons from Interreg Projects ERUDITE and CARPE DIGEM

Local stakeholder event in Västernnorland, Sweden
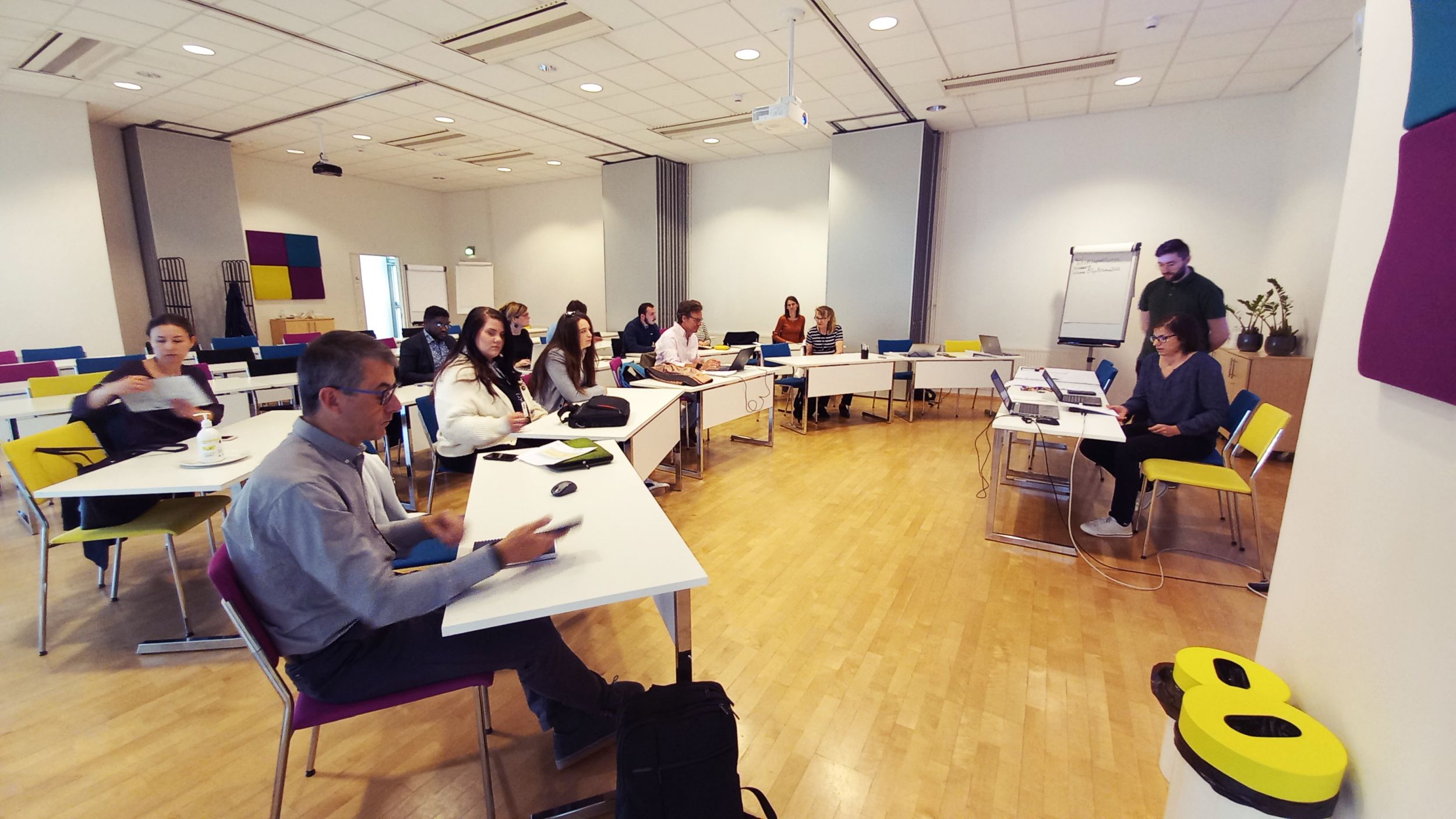

Summary of the partnership event held in Seiäjoki, Finnland

A Policy Brief from the Policy Learning Platform on Research and innovation

Nièvre Stakeholders Health and Care Study Visit: to Västernorrland 05-06 December 2021
Analysis and exchange of experience to design implementation strategies with focus on digital services in rural and peripheral regions.

How to achieve digitalization-driven innovation in a countryside city.

Erudite Finale Project Coordination Meeting in Venice on 23-24 January 2020