
SET-UP is over: 6 years of successful collaboration
Supporting businesses and citizens in the energy transition is a key result of this long-lasting, interregional collaboration.
The overall goal of the SET-UP project is to improve energy performance of the 6 partner regions thanks to enhanced policies on smart grids. On a medium to long term, better energy demand management achieved thanks to SET-UP will lead to reduced energy consumption and greater energy security, with connected socio-environmental and economic benefits.
SET-UP uses interregional exchange to build on regional competencies on smart grids, supported by selected regional policy instruments (ERDF ROP, Axis on energy / low carbon). SET-UP improves policy instruments by identifying efficient energy management tools, with a specific focus on solutions to 3 main challenges to smart grid deployment:
Various activities for interregional exchange, communication and stakeholder engagement (with business sector engagement), help partners to develop regional Action Plans. These plans result in improved policy instruments supporting regions in their attempt to design, implement and direct more and better funding towards integrated smart grid strategies.
€1,645,220.00
Low-carbon economy
Smart grids are energy networks that automatically monitor energy flows and adjust to changes in energy supply and demand accordingly. With smart grids, the potential for energy monitoring, energy saving and integration of energy from renewable sources is huge. Potential benefits are clear, and various European initiatives have been launched to take advantage of them.
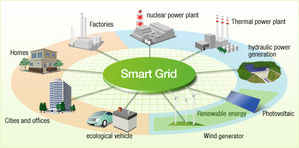
However, integrated regional low-carbon strategies are needed to identify suitable actions for a specific territory, to channel public and private investments and to increase the awareness of and mobilise public and private stakeholders (from the business sector, to local citizens). Strategic integration of ICT-based low-carbon innovations should also be accelerated.
SET-UP supports 6 regions, at different stages of smart-grid development, to face these common challenges together.
Brittany’s investment for Growth and Jobs Programme ROP 2014-2020 aims to strengthen the coherence between investment and the structural reforms priorities and focuses on the need to promote growth and employment in order to achieve Europe 2020 strategy objectives.
Priority axis 3 “Improve energy and ecologic transition in Brittany” supports the aim to produce 20% of its primary energy and 34% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2020, in line with EU targets.
Priority Axis 3 has three specific objectives: increase RES development, decrease the carbon impact of buildings and support sustainable transport.
Within the framework of specific objective 3.1 “increase the production of RES”, the development of smart grids is identified as one of the major priority for the energy transition strategy. Large and small scale Smart grids and energy storage projects are, therefore, specifically mentioned by action 3.1.1 “Improving RES production and distribution capabilities in Brittany”. Beneficiaries will be regional enterprises, local governments and territories and associations.
Priority axis 5 ‘Increasing energy efficiency and the use of renewable energy sources’ of the Hungarian Environmental and Energy Efficiency Operational Programme (EEEOP – finance by ERDF) has 3 specific objectives: increasing the use of renewable energy sources (RES), increasing energy efficiency and raising awareness on eco-conscious behavior.
In the framework of the first objective it supports production of green energy, small capacity energy storage systems, small-scale demonstration projects for new energy production technologies, and project preparation activities. Action 5 of the priority aims to ‘Support smart grid systems to improve the flexibility of the electricity grid’.
For the calls of this action different legal entities (i.e. central budgetary institutions, the transmission system operator, distribution system operators, power plants and telecommunication companies) are eligible.
The aim of the CRESC Algarve 2020 is to generate consensus and mobilise the region for a balanced development. The main objective is to transform Algarve to be a more competitive, resilient, entrepreneurial and sustainable region based on the value of knowledge.
Though Priority Axis 4 and the specific measure 4C, CRESC Algarve 2020 supports energy efficiency, the intelligent management of energy and the use of renewable energy use in public infrastructures of Local Administration.
It is noted that Algarve is at the start of discussion on smart grid implementation. The priority exists in the region, but work is needed to implement it. In particular, this could be achieved by linking the priorities on intelligent management with the priority of public infrastructures.
In the 2014-2020 programming period, Lithuania will seek to invest in smart electricity distribution network management technologies that offer new services to consumers, facilitate their active participation in the electricity market and enable a more efficient and smooth grid management.
INVESTMENT PRIORITY 4.1 focuses on developing and implementing smart distribution systems at low and medium voltage levels. Within this, specific objective 4.4.1 tests the prospects of introducing smart grid technologies. These could include active/integrated systems for monitoring equipment, technologies to support autonomous grid modes, diagnostic technology, fault detection devices and management technology for smart buildings.
Although the selected policy instrument and related priority support actions for the introduction of smart grid technologies, Lithuania finds itslef at the start of discussion on implementation of smart grids.
The LLEP is responsible for the new round of European Structural Investment Funds (ESIF) in Leicester and Leicestershire.
One of the priorites for the LLEP is developing SMART Environmental Technology and Supply Chains. This will be done through developing the economic low carbon sector and also growing the demand for these services. It is firmly believed that this sector needs to continue to grow locally. To support its growth we will need to maximise the use of SMART systems to help make Leicester a low carbon city and Smart city.
In addition the City Council has an aim to reduce carbon emissions by 50% based on 1990 levels. A smart city for Leicester means: rolling out smart meters, city wide Wifi, intergarted Smart card (for travel, access to services etc) and a virtual power plant and smart grid for data and BMS.
The main objective of the selected policy instrument is to develop an energy infrastructure system that ensures quality of supply and use of autochthonous resources of Andalusia, as well as its orderly implementation in the territory, forming a more efficient energy model through the incorporation of elements that allow for "smart" energy management.
The policy instrument addressed forms parts of regional energy strategies and planning of the Regional Government. Under priority 4.d, actions associated with smart energy networks and improving the quality of energy supply will be financed.
Experiences from previous programmes advises that the following improvements in the new operational programme should be made:

Supporting businesses and citizens in the energy transition is a key result of this long-lasting, interregional collaboration.

The role of transnational R&I networks to strengthen smart energy

Webinar organised by our Advisory partner Regen and the Policy Learning Platform.

The SET-UP Smart Energy conference has been held in Brussels on 20th of March 2019.

SET-UP partners Regen and Andalusian Energy Agency delivered a presentation on electric vehicles and the electricity system.

Our partner AREAL, from the Algarve region in Portugal, presented SET-UP during this major event about mobility.
SET-UP partners met in Lithuania for their 6th project meeting.

Our partner AREAL attended the National Meeting of Energy and Environment Agencies.

Organised by our Advisory partner Regen, the conference focused on energy transformation.

Our partner TCDA has been invited to introduce SET-UP and the Hungarian Smart Synergy project.