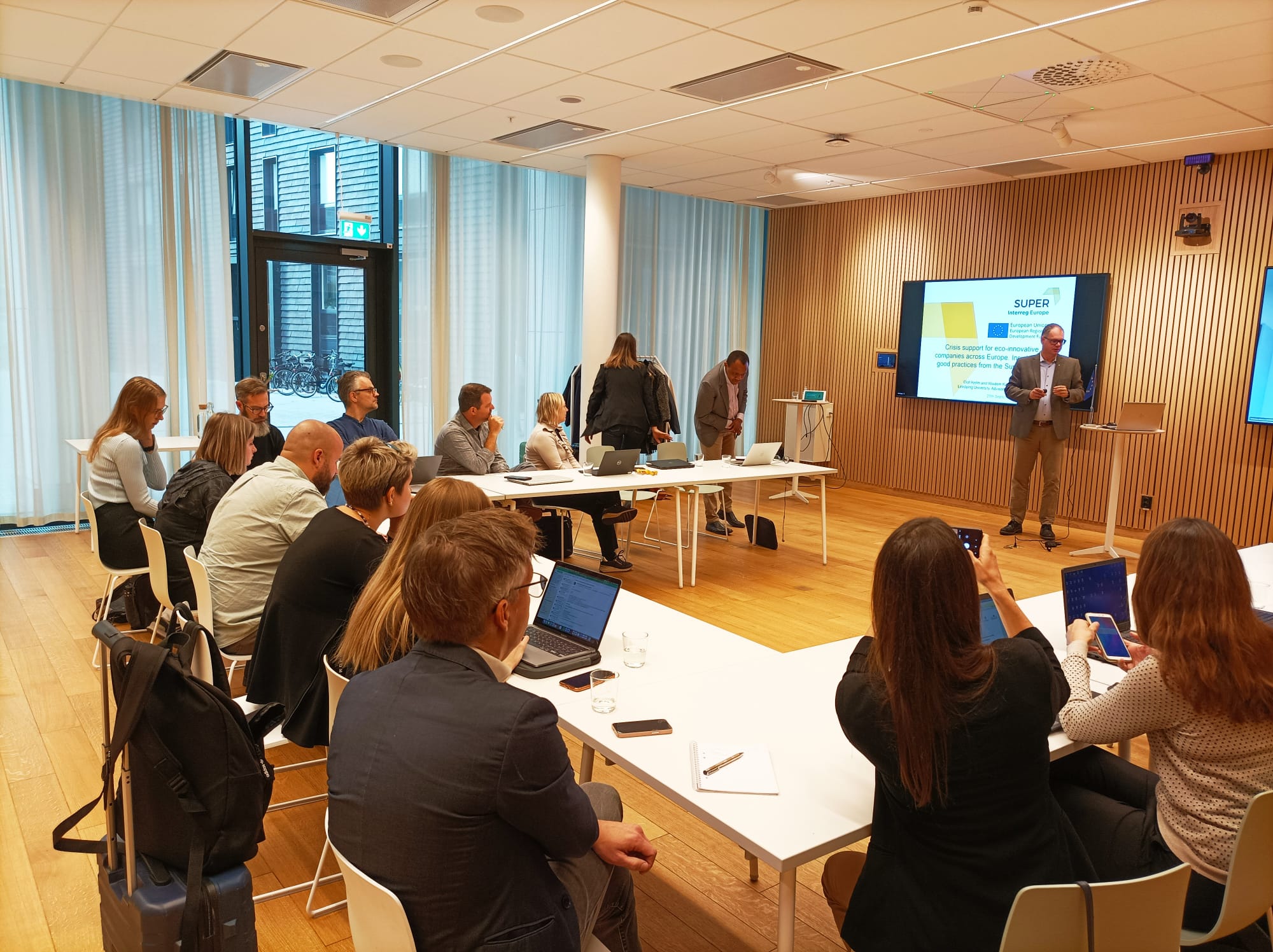

SUPER Project Final Conference
On September 28-29, 2022 the final conference of the second phase of the SUPER project took place in Linköping (Sweden)
We aim to improve SMEs uptake of Environmentally Sustainable Innovations (ESIs) into their business. For that the regions need to work further on how to develop models such as the cooperative business support model, where the focus should be on possible measures for business development and how companies can evolve towards an Environmentally Driven Export Market (EDEM) while working together with the whole chain of support and in close interaction with the SMEs themselves. Herein lays a need to create an international network of contacts concerning how public and private bodies can work on these issues in order to improve policy delivery for an Environmentally Driven Business Development of SMEs.
EDBD implies an instrumental meaning; the purpose is to develop the businesses by developing the environmental dimension in their use of technology, in their business dealings, and their markets, i.e. the environmental aspect is a tool to develop business. As such, EDBD does not only include Clean Technologies, but also product development in other fields of business that utilize an environmentally friendly approach.
The above will be accomplished thru exchange of experiences and practices, benchmarking and analysis of challenges and needs.
€1,883,324.00
Research and innovation
Operational programme Growth and employment 2014-2020:
Priority Axis 1. Development and innovation of research, technology :
Thematic objective 1.Strengthening research, technological development and innovation:
Investment priority 1.2.: Specific objective (SO) No. 1.2.1.: To promote investments of private sector in R&D
Indicative actions to be supported: support for research according to the needs of the private sector, for development and implementation in production of new products, services, technologies and processes, including innovation vouchers for SME, ensuring technology transfer services within the framework of a single technology transfer system, including protection of newly created intellectual property, preparation and submission of licenses and certificates, preparing of research results with commercial potential for licensing, creating opportunities for networking of education and research institutions, students and entrepreneurs for development, testing and implementation in the market of innovative interdisciplinary products and services.
Approximately 10% of the Danish companies have collaboration with knowledge institutions, but the majority of the 10% refers to companies in the capital region whereas companies in Region Zealand have much less collaboration resulting in a lower product development rate, lower investment in R&D and lower overall innovation rate.
Axis no. 1: Strengthening research, technological development and innovation.
Investment priority 1.2.: Specific objective (SO) No. 1.2.B.: Actions to promote research
and innovation in SME’s in priority areas of the RIS3
MA of RWM will prepare a Regional Action Plan (RAP) for Axis 1 structural funds of the regional operational programme that will combine the project SUPER objectives. The main objective of Axis 1 is meeting the needs for achieving the objectives
Europe 2020 RTDI by increasing the level of investment on research to GDP for 2020 proposed by the RIS3 plan (internationalization, regional structures for innovation support, incubators, direct co-financing etc). Main characteristics & priority of the specific RAP (outcome of the project), include activities to EDBD that will focus on Green Energy Buildings (public and private) and to some manufacturing sectors related with energy products or services.
The policy instrument should be improved (as other instruments also) with the regional structural funds of the period 2014-2020 as research and innovation were of low priority in the regional policy agenda until 2014, due to the lack of authority in this domain of policy and the weak capacity of the regional administration. For the first time Greek Regions and managing authorities are responsible for the policies instruments they want to improve in RTDI.
PRIORITY AXIS 1The analysis of the present socio-economic situation, challenges and potential for development in Lithuania clearly demonstrates that the Lithuanian economy and society still feel the consequences of the recent financial and economic crisis. The main aim of this programme is to bring the country back to the path of rapid and sustainable growth and to reduce the gap between country’s level of development and the EU average. This requires sustaining a stable macroeconomic environment, continuing structural reforms and ensuring adequate financing for growth measures.
Priority No. b) Promoting business investment in R&I, developing links and synergies between enterprises, research and development centres and the higher education sector, in particular promoting investment in product and service development, technology transfer, social innovation, eco-innovation, public service applications, demand stimulation, networking, clusters and open innovation.
LECP) for County Tipperary is to set out, for a six-year period, the objectives and actions needed to promote and support the economic development and the local and community development of the county, both by the County Council itself directly and in partnership with other economic and community development stakeholders.
It is set out in law that the Plan shall be for the promotion of economic development and the promotion of local and community development.
The LECP is part of a series of plans and strategies that have, and are being developed, at national, regional and local level.
These include:
-The National Spatial Strategy, National Development Plan, Rural Development Strategy, the Action Plan for Jobs and the National Anti-Poverty Strategy
-The Regional Spatial and Economic Strategies
-The City (County) Development Plan made under the Planning Acts
- The local Education and Training Strategy.
The main objective of the ROP for Podlaskie Voivodeship is to increase economy competitivnes by regional specialisations.
Priotity axis I Strengthening Potential and Competitiveness of Region`s Economy
Action 1.b. Promoting the transfer of knowledge, innovation, technology and commercialization of R&D results and development of R&D activities
Podlaskie Voivodeship’s has high quality natural environment. The care necessary to maintain the environment’s high quality is an important factor increasing the opportunities for the competitive economy to expand, especially in “green” sectors. The activities that are taken to increase regional development should point innovation process in region to be more focused on innovation and environmentally friendy innovations issues. The SMEs that are one of the beneficiaries of the OP should not only be focused on innovations that enhance their competitiveness but also on innovations with environmental dimension and should also increase ability of SMEs to formulate their eco-innovation ideas and relize them.
This project should influence increased investments in new eco-innovations both in the form of ready to use solutions and in the form of R&D independently undertaken by companies or research institutions or within the framework of their cooperation. The interaction within these two sectors: science and business is very important..
Thematic objective 1.Strengthening research, technological development and innovation
Investment priority 1.2.:Promoting business investment in R&I, developing links and synergy between enterprises, research and development centres and the higher education sector, in particular promoting investment in product and service development, technology transfer, innovation, eco-innovation, public service applications, demand stimulation, networking, clusters and open innovation through smart specialisation, and supporting technological and applied research, pilot lines, early product validation actions, advanced manufacturing capabilities and first production, in particular in key enabling technologies and diffusion of general purpose Technologies.
Specific objective (SO) No. 1.2.1.: To promote investments of private sector in R&D.
SO No. 1.2.1.: supports actions for research according to the needs of the private sector, for development and implementation in production of new products, services, technologies and processes, networking of education and research institutions and entrepreneurs for development, testing and implementation of innovative interdisciplinary products and services. However SO does not specifically address the needs and potential of commercialization and internationalization of environmentally driven businesses, through comprehensive regional support systems.
This instrument is set up to stimulate sustainable economic growth in the Utrecht region with a focus on 1)Green economy, 2) smart society and 3) healthy society. All the funds for economic development (€ 17 million) have been allocated for this instrument.
The regional government of Utrecht is responsible for regional policies that help support SMEs innovate and accelerate towards a more sustainable future The regional government decided to place funds for SME support in a separate body (Economic Board Utrecht) where in triple helix setting funds can be more efficiently directed towards the SMEs.
The board employs several instruments in order to help support the transition. The ‘Uitvoeringsverordening Economic Board Utrecht’ provides the legal framework for all the instruments employed. The Uitvoeringsverordening can thus be seen as an umbrella instrument under which more specific instruments can be developed. This approach has been successful because we are able to identify an obstacle and make and specific instrument to solve it. Instruments in the Uitvoeringsverordening that support SMEs are:
• feasibility studies
• innovation advisory projects
• R&D-related cooperative projects
• financial support (subsides)
However, there is always room for improvement and we are searching for policies that are able to support those companies that are most likely to be successful and help speed up our agenda.
Thematic Objective 1 of the Operational Programme
01 - Strengthening research, technological development and innovation
Investment priority
“1b - Promoting business investment in R&I, developing links and synergies between enterprises, research and development centres and the higher education sector, in particular promoting investment in product and service development, technology transfer, social innovation, eco-innovation, etc...S
Specific objective: Encouragement and promotion of R&D activities leaded by enterprises, support to innovative business creation and consolidation and support to public innovative acquisition
In the strategic lines is defined the need to redress the existing shortcomings in the region on environmental issues identified in the PERM (climate change mitigation, improved waste management and biodiversity protection) is present. However, it is necessary to define concrete actions to implement sustainable business policies.
To this end, we should develop measures to improve business competitiveness of SMEs implementing policies and management models of sustainable development and both active development and uptake of eco-innovations.
The proposed measures focus on:
•Training and business advice on the competitive advantages that involve the implementation of sustainable development policies the use of eco-innovations and operating on international markets
Priority axis 1: Promoting Research and Innovation
Investment Priority 1b – Promoting business investment in R&I; developing links and synergies between enterprises, research and development centres and the higher education sector, in particular promoting investment in product and service development, technology transfer, social innovation, eco-innovation, public service applications, demand stimulation, networking, clusters and open innovation through smart specialisation; and supporting technological and applied research, pilot lines, early product validation actions etc.
specific objective: Increase of innovation activities among SMEs with growth ambitions and conditions for commercialisation of innovations
The challenges identified in east mid Sweden in the analysis prior to the OP was that there is a need to strengthen cooperation between the private and public sectors and the academia in order to increase innovation, that there is a need to increase SMEs innovation capacity, that their investments in R&D are relatively low, that investments in organizational, market and social innovations is lower than in technological innovations and that the commercialization of innovations is weak. With the activities in the SUPER project we intend to adress a number of these challanges, particualry working on the issues of strengtening cooperation between the different actors and working on the issue of commercialization and internationalization of eco-innovations.

On September 28-29, 2022 the final conference of the second phase of the SUPER project took place in Linköping (Sweden)
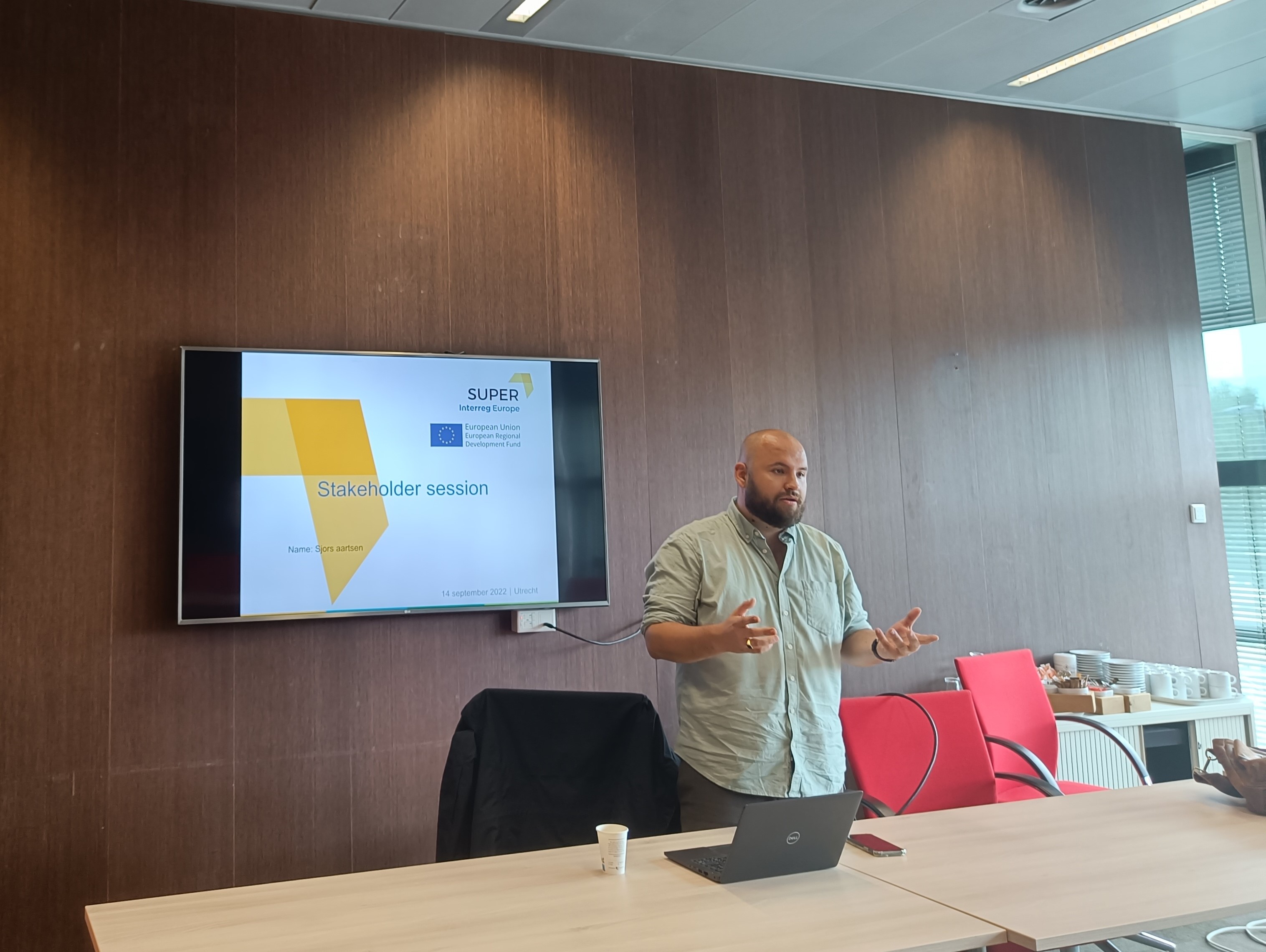
Regional workshop with stakeholders in the province of Utrecht, the Netherlands
Regional workshop with stakeholders in Murcia, Spain
Entrepreneurs of Vidzeme region value Covid-19 support for its improvement in the future
On March 31, the SUPER partnership met at the premises of CEEIM in Murcia, Spain, for an interregional partner meeting.
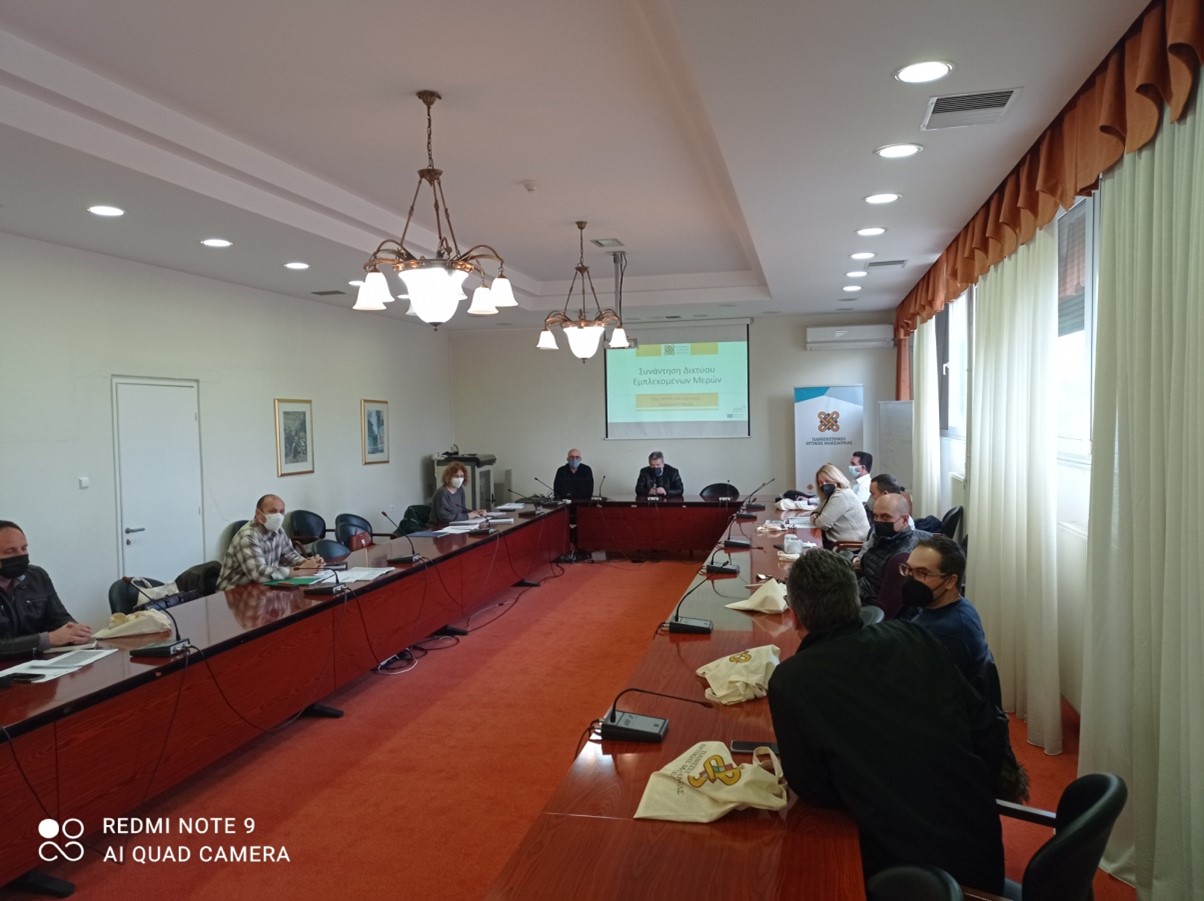

The first SUPER stakeholder meeting in Greece took place on the 21ST of February 2022. Eight (8) participants from the stakeholders’ side were present.

As we reach the end of the project, we have asked the project partners to summarise their main learnings and results from the project and how they have benefite...

As we reach the end of the project, we have asked the project partners to summarise their main learnings and results from the project and how they have benefite...

As we reach the end of the project, we have asked the project partners to summarise their main learnings and results from the project and how they have benefite...

As we reach the end of the project, we have asked the project partners to summarise their main learnings and results from the project and how they have benefite...