Navarra is committed to sustainability and the fight against climate change.
Aimed at a new socioeconomic and energy model with a low carbon economy and adapted to the effects of climate, it seeks to be a point of reference for sustainable development, with an environmentally responsible and efficient territory in the use of resources, with a balance between people, their activity and the environment in which they are based. These objectives are in line with the Smart Specialization Strategy (S3) and the social policies of the Government of Navarre. Furthermore, in direct relation to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development (SDGs), adopted by all United Nations Members States in 2015.
Navarre regions have been working to align its policy to the Green Deal and make of Europe a sustainable economy. It can highlight five policy instruments where life cycle thinking is included.
1. Agenda for the development of the Circular Economy in Navarre 2030.
This agenda has six strategic objectives:
- Sustainable and efficient management of natural resources.
- Replace fossil fuels with renewable ones.
- Reduce waste generation and increase recovery.
- Increase responsible consumption in the public and private sectors.
- Extending the culture of sustainability.
- Contribute to sustainability (economic, social and environmental) and territorial cohesion.
To achieve these objectives, a series of actions will be defined, through the elaboration of biennial work plans, to develop the challenge on circular economy.
2. Waste Plan of Navarre 2017-2027
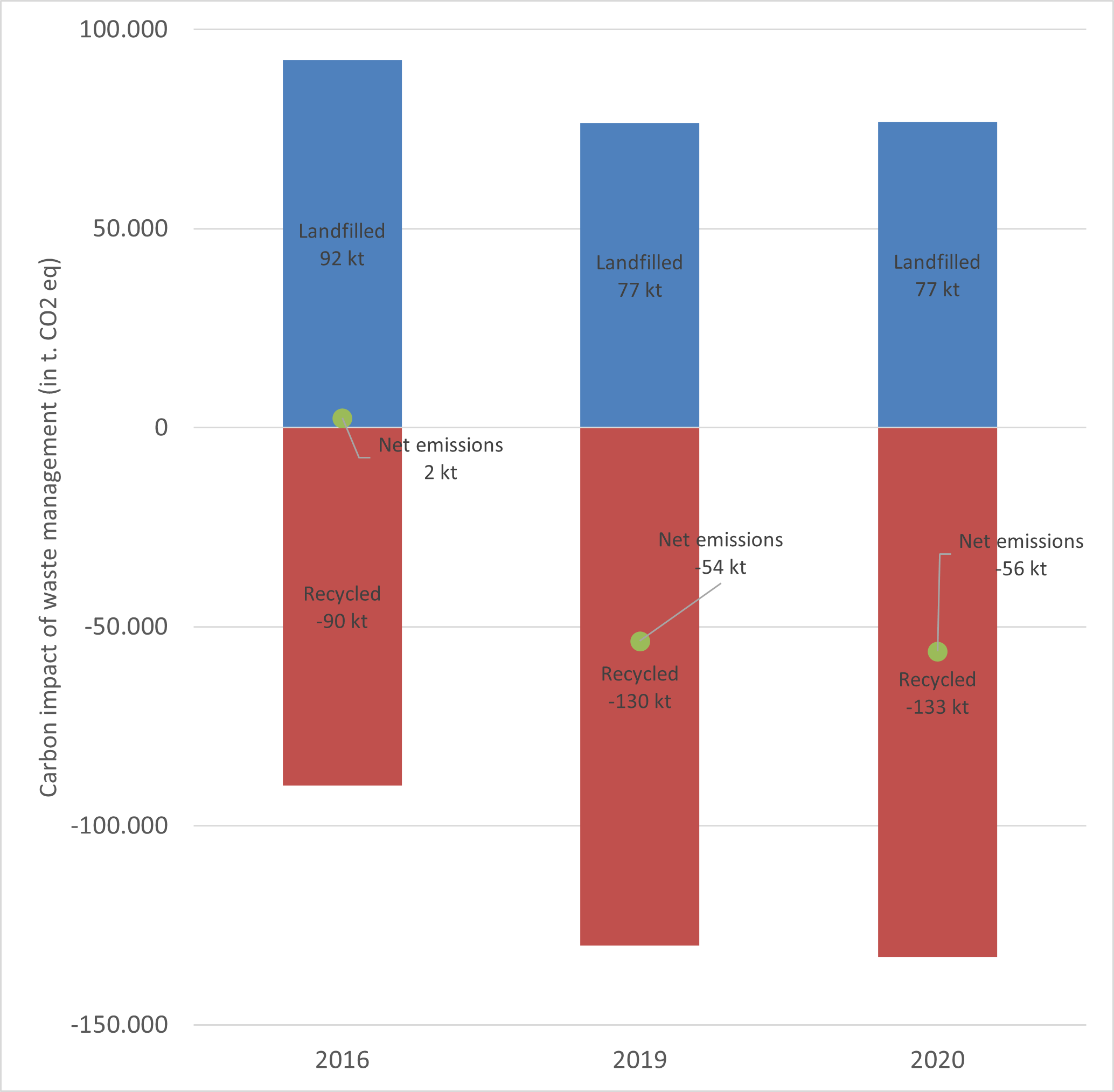
The Waste Plan of Navarre aim is to convert Navarra into an efficient society in the use of resources that produces less waste and uses as resources those that cannot be avoided, create green jobs and contribute to the strategy against climate change.
The calculation of the carbon footprint associated with waste management has been included for the first time as a planning tool, both in infrastructure, as in events, transport, and in the collection models themselves.

3. Regional Law on Waste and its Taxation
This newlaw ensure the effective application of the waste management hierarchy through specific prevention measures and set up three innovative measures:
- The creation of a waste prevention office to impulse the circular economy.
- Establish a new taxation system that penalizes waste sent to landfill and creates a Waste Fund to mitigate the waste-related adverse impacts on human health and the environment.
- Promotion of Green public procurement prioritizing reusable materials and recyclable products in their purchases.

4. Public Contracts Law
This foral law includes for the first time the concepts of life cycle and life cycle cost that includes all costs throughout the life cycle of works, services and supplies.
These costs can be both internal (including research and development, production, transport, energy consumption, maintenance and disposal) as well as those related to external environmental factors (for example, greenhouse gas emissions, pollution derived from the extraction of raw materials or that produced by the manufacture of the product).
5. Climate Change Roadmap 2030-2050-KLINA.
The roadmap establishes mitigation objectives to stimulate and accelerate as far as possible the transition to a decarbonized economic, social and environmental development model; and adaptation objectives, following the European Strategy for Adaptation to Climate Change (2013) and adapting it to our reality and territorial scale.
According to the European strategy on climate and energy, Navarra is working on the development of the Navarra Horizon 2030 Energy Plan, which pursues a series of objectives to improve the energy situation and reduce its GHG emissions and impacts on the climate.
Challenges
On the work Navarre regions is doing to be a more environmentally friendly economy, there are some improvement:
- Engage all administrations that work with the different economic sector to follow and impulse life cycle approach in the daily management of organisations.
- Incentive or support companies that are using life cycle methods.
- Establish simple and user-friendly life cycle tools to be able to apply in an easy way the Public Contracts Law.
- Define life cycle approach obligations for infrastructure authorizations to companies.
- Define and priorities circularity criteria for the projects or companies that ask for support thank to the Waste Fund from the Regional Waste Law.
Know more: